ACE2: A predictor of infectability in SARS-Cov-2
Jul 13, 2022

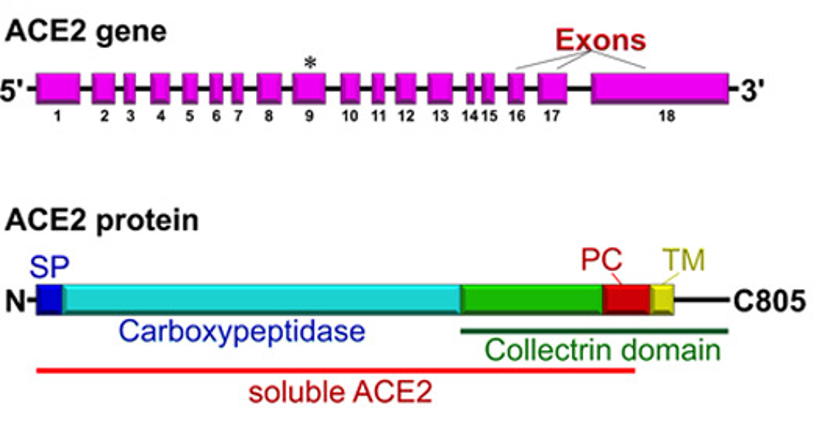
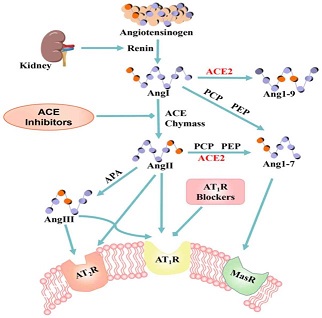
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2), is a single-pass type I membrane protein and a zinc metalloprotease of the ACE family. ACE2 encodes for a protein that catalyzes the cleavage of angiotensin I into angiotensin 1-9 and angiotensin II into vasodilator angiotensin 1-7. Human ACE-2 protein consists of 805 amino acids, including a N-terminal signal peptide, a single catalytic domain, a junctional segment of the collectrin domain, a peptidase cleavage site, a TM domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. It’s theoretical molecular weight: 92 kDa.The encoded protein is a functional receptor for the spike glycoprotein of the human SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19).
Scientific Significance of ACE2
ACE-2 also serves as the receptor for the SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Binding of the S1 domain of the SARS Coronavirus Spike protein to ACE-2 initiates viral entry into the host cell.
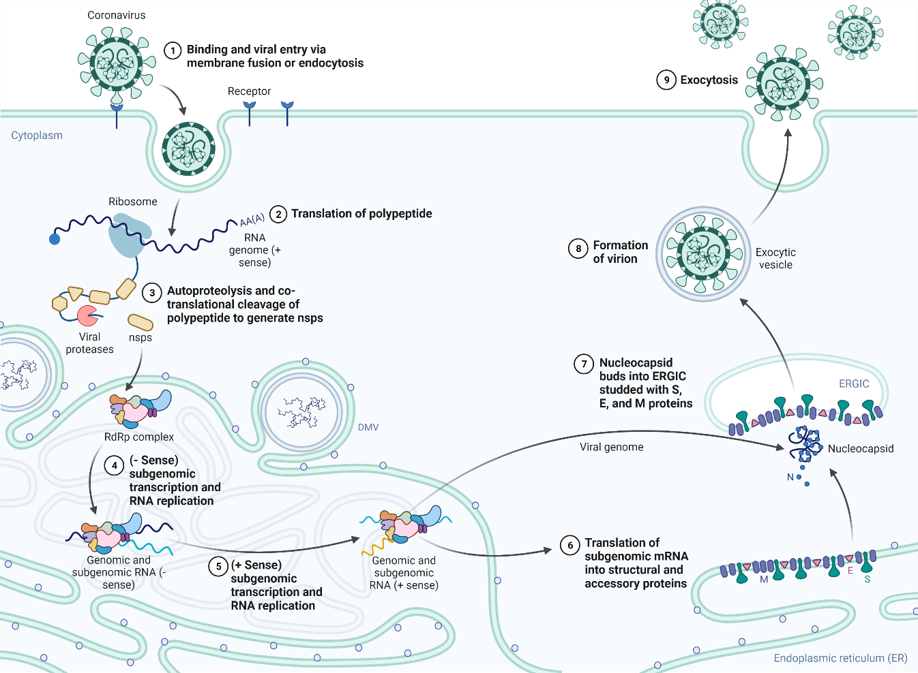
Hypothesis of ACE2 shedding and SARS-CoV-2 entry.
Cellular ACE2, ADAM17, and TMPRSS2 are all expressed on the cell membrane. After being shed by ADAM17, soluble ACE2 is released from its full-length form to counteract the effects of Ang II signaling. Alternatively, cellular ACE2 is also shed by TMPRSS2, which results in SARS-CoV-2-cell membrane fusion. SARS-CoV-2 RNA is then released into the cytoplasm and viral replication is efficiently processed. Because soluble ACE2 contains the virus binding site, it can also bind to the virus. However, without an intracellular environment, the virus cannot be duplicated.
The primary organs or tissues expressing ACE2 include the heart, lung, brain, oral cavity and nasal mucosa, nasopharynx, kidney, stomach, small intestine, colon, skin, lymph nodes, thymus, bone marrow, spleen, liver and blood vessels.
ACE2 plays a central role in vascular, renal, and myocardial physiology. ACE2 has good potential for use in the treatment of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal malnutrition and other viral‑related symptoms.
Several findings suggest that rhACE2 may be a promising drug for those with intolerance to classic renin-angiotensin system inhibitors (RAS inhibitors) or in diseases with elevated angiotensin II. Infused rhACE2 has been evaluated in clinical trials for the treatment of ARDS.
Recently, ACE-2 has become an area of intense therapeutic interest to develop treatments against COVID-19. An in vitro study found that clinical-grade human recombinant soluble ACE2 (hrsACE2) reduced SARS-CoV-2 recovery from vero cells by a factor of 1,000-5,000. Some drugs including remdesivir, lopinavir, sofosbuvir, and daclatasvir that can block the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein to the human ACE2 receptor, are undergoing clinical trials.
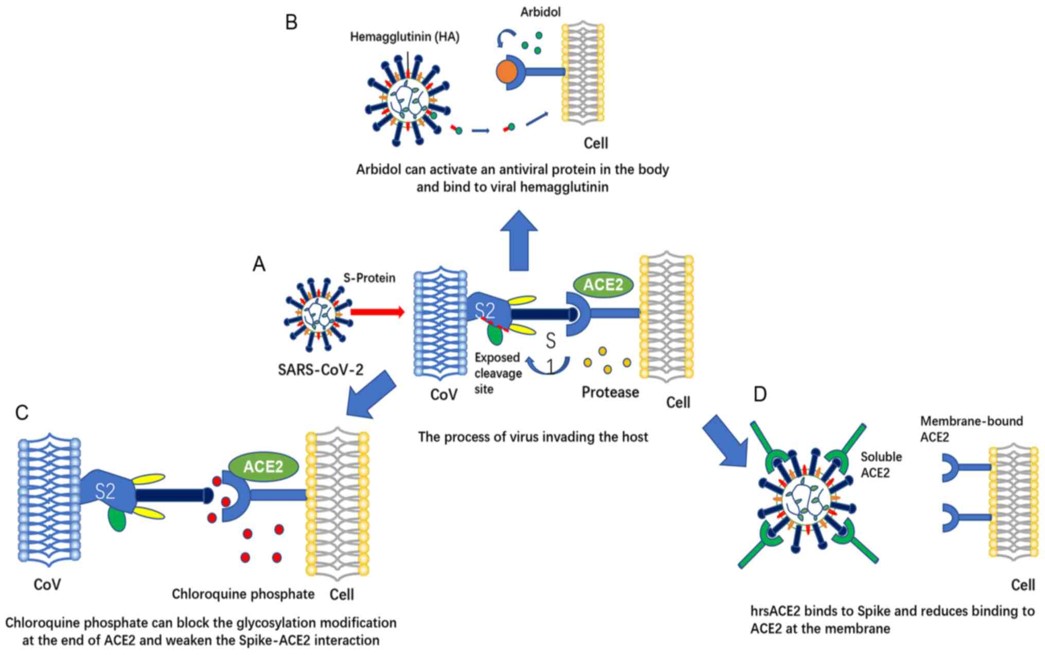
| Name | Arbidol (ARB) | Chloroquine phosphate (CQ) | Clinical-grade soluble human ACE2 (hrsACE2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Spike-ACE2 and Affect the virus life cycle | Inhibit the process of virus replication and block terminal glycosylation modification of ACE2 | Inhibit lung damage and prevent virus invasion |
| Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data | EC50=10 μM CC50=20-100 μM | EC50=1.13 μM CC50=100 μM | Not reported (currently undergoing Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials; NCT00886353, NCT01597635) |
| Applicable stage | Early stage of viral infection | Pneumonia worsening stage | Prevent infection stage; late lung injury stage |
| Suggested dose | 200 mg/day <10 days for adults | 1,000 mg/day (twice) for 7 days | 25-200 μg/day |
| Possible adverse reactions | Not reported | May increase the risk of fatal ventricular arrhythmia | May increase the risk of virus infection |
| Problems to be solved | Standardized animal studies and controlled clinical trials | The gap between in vitro antiviral activity and clinical effect; standardized diagnosis and treatment plan yet to be formulated | The impact of hrsACE2 in the later stages of the disease process |
Under Covid-19 infection ACE2 receptor acts as a potent membrane receptor used by the virus to bind and enter the host cells via endocytosis. This decreases the availability of ACE2 receptors on cell membranes resulting in loss of membrane-bound catalytic activity.
Moreover, a study found that the serum levels of ACE2 are significantly higher in highly exposed but uninfected subjects suggesting that high levels of ACE2 in serum may somewhat protect against an active infection without generating a conventional antibody response.
ACE2 Resource Tool Center
Assay Kits for ACE2
OriGene's ACE2 ELISA kit provides sensitive and reliable ACE2 measurements to obtain valuable data from your experiments.
Get your ACE2 Elisa Kit hereAntibodies for ACE2
OriGene has developed highly-specific and sensitive antibodies that recognize native epitopes which can be used in IHC, ELISA, WB. IF, IP etc
Primary Antibodies
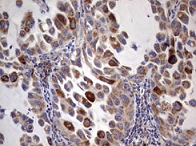
Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded Carcinoma of Human lung tissue using anti-ACE2 mouse monoclonal antibody.
Carrier-Free Antibodies
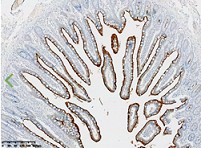
Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded Human colon tissue within the normal limits using anti-ACE2 mouse monoclonal antibody.
Primary Antibody Samples
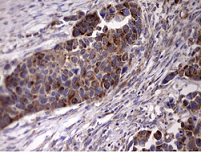
Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded Carcinoma of Human kidney tissue using anti-ACE2 mouse monoclonal antibody.
Clones for ACE2
OriGene has developed expression ready plasmids and Lentiviral particles for various species such as human, mouse and rat species.
Tagged/Un-Tagged Clones

HEK293T cells were transfected with the pCMV6-ENTRY control (Cat# PS100001, Left lane) or pCMV6-ENTRY ACE2 (Cat# RC208442, Right lane) cDNA for 48 hrs and lysed
Lentiviral Particles
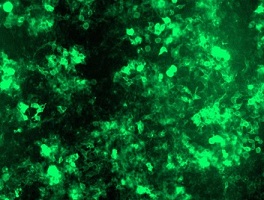
RC208442L2 was used to prepare Lentiviral particles using TR30037 packaging kit. HEK293T cells were transduced with RC208442L2V particle to overexpress human ACE2-mGFP fusion protein.


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China