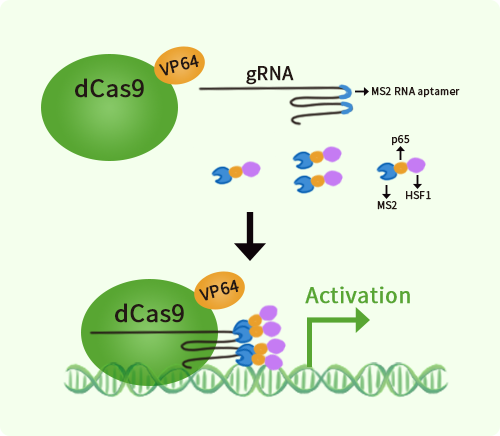
Human Nogo B receptor (NUS1) activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA114569
NUS1 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human NUS1 dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase subunit
CNY 12,255.00
CNY 1,999.00
CNY 2,700.00
CNY 2,400.00
CNY 3,990.00
CNY 800.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3 gRNAs (5ug each), 1 scramble ctrl (10ug) and 1 enhancer vector (10ug) |
| Symbol | NUS1 |
| Locus ID | 116150 |
| Kit Components | GA114569G1, Nogo B receptor gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA114569G2, Nogo B receptor gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA114569G3, Nogo B receptor gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPRa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_138459 |
| Synonyms | C6orf68; CDG1AA; MGC:7199; NgBR; TANGO14 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a type I single transmembrane domain receptor, which is a subunit of cis-prenyltransferase, and serves as a specific receptor for the neural and cardiovascular regulator Nogo-B. The encoded protein is essential for dolichol synthesis and protein glycosylation. This gene is highly expressed in non-small cell lung carcinomas as well as estrogen receptor-alpha positive breast cancer cells where it promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition. This gene is associated with the poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation and are associated with epilepsy. A knockout of the orthologous gene in mice causes embryonic lethality before day 6.5. Pseudogenes of this gene have been defined on chromosomes 13 and X. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017] |
Documents
Resources
| 基因表达相关资源 |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN424928 | NUS1 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
CNY 8,680.00 |


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China