Human APO-1/FAS ELISA Kit (96-well)
CNY 3,990.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Description | Human APO-1/FAS ELISA Kit (96-well) |
| Size | 1 x 96 wells |
| Format | 96-well strip plate |
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Signal | Colorimetric |
| Curve Range | 62.5-4000pg/ml |
| Sample Type | Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin) |
| Sample Volume | 20 uL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant Human APO-1/FAS Ligand |
| Sensitivity | 31pg/mL |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules. |
| Components |
|
| Background | Apoptosis inducing protein 1(Apo-1) also known as Fas (Fibroblast-associated), CD95, and TNFRSF6(325 amino acids, 45-48 kDa), was originally identified as a cell-surface protein that binds to monoclonal antibodies that are cytolytic for various human cell lines. Fas is expressed by a broad range of hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells including monocytes, neutrophils, activated lymphocytes and fibroblasts. Interaction of Apo on mature lymphocytes with its ligand (FasL) induces apoptosis and is thought to be important in peripheral tolerance. Fas-mediated death occurs much more rapidly than that triggered by TNFR1(Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1). Fas (APO-1 or CD95) is a cell-surface receptor that transduces apoptotic signals from Fasligand (FasL) . It is a glycoprotein with a mass estimated at 43 to 48 kDa . Fas is a member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily (TNFRSF), and it shares a cytoplasmic motif with TNF RI, referred to as the Â?death domainÂ?, that binds cytoplasmic signaling molecules to trigger the cytoplasmic apoptotic signal . Fas is expressed to a large extent on activated T and B lymphocytes, and on malignant lymphoid cells. To a lesser extent, Fas is expressed on cells from liver, heart, kidney, ovaries, and on many other malignant cells. FasL, the physiological agonist for Fas, is also a transmembrane protein with homology to the TNF family in its extracellular domain. FasL is expressed primarily by activated T lymphocytes and by cells of the small intestine and lung. Mice with mutations in either Fas or FasL exhibit accumulation of activated lymphocytes and classical autoimmune symptoms, suggesting that a major function of Fas-mediated apoptosis is the elimination of activated immune cells from the peripheral circulation . Similarly, humans with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome have mutations in Fas . Fas and FasL have been observed as soluble molecules in addition to their membraneassociated forms, suggesting additional complexity to regulation of this apoptotic mechanism . Soluble Fas (sFas) arises from alternatively spliced mRNA, leading to proteins with deletion or disruption of the single membrane-spanning domain . Five alternatively spliced Fas mRNAs have been described , each protein detected in the supernate of cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells or certain tumor cell lines. Each sFas inhibited apoptosis induced by FasL , and tumor-cell lines resistant to anti-Fas were shown to produce alternatively spliced Fas, thereby making them less sensitive to FasL. In addition, plasma Fas can arise by exfoliation of membrane vesicles, which also inhibit FasL-induced apoptosis . Serum Fas has been reported to be elevated in cancer patients , possibly originating in the tumor cell itself , and in autoimmune diseases . |
| Gene Symbol | FAS |
| Standard Curve |
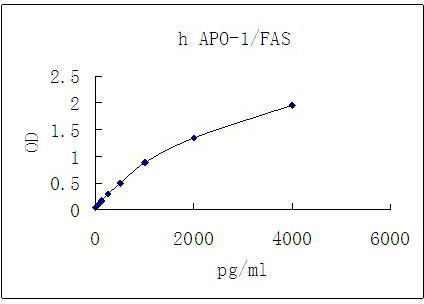
Representative standard curve for APO-1/FAS ELISA. APO-1/FAS was diluted in serial two-fold steps in Sample Diluent.
|
Documents
| Product Manuals |


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China

