Rat IL-1a ELISA Kit (96-well)
CNY 3,990.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Description | Rat IL-1a ELISA Kit (96-well) |
| Size | 1 x 96 wells |
| Format | 96-well strip plate |
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Assay Length | 3 hour |
| Signal | Colorimetric |
| Curve Range | 0.02 - 1.0 ng/mL |
| Sample Type | Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin) |
| Sample Volume | 20 uL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant Rat IL-1a Ligand |
| Sensitivity | 7pg/mL |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules. |
| Components |
|
| Background | Interleukin-1. (IL-1., also known as IL-1F1) and IL-1. (IL-1F2) are pleiotropic cytokines that belong to the IL-1 gene family. IL-1. and IL-1. bind to the same cell surface receptors and share biological functions. The two proteins have approximately 23% amino acid (aa) sequence homology and both are synthesized as 31 kDa precursors that lack hydrophobic signal peptide sequences. Current evidence suggests that IL-1 proteins may be secreted via non-classical pathways . Rat IL-1. cDNA encodes a 270 aa residue pro-IL-1. precursor . The 114 aa pro-region contains a nuclear localization sequence, a lysine-based myristoylation site, one phosphorylation site, and one potential N-linked glycosylation site . The 156 aa mature region contains no cysteines and one potential N-linked glycosylation site . Pro-IL-1. is primarily localized to the cytosol after synthesis. It is known to translocate to the nucleus after cell activation and initiate gene transcription . Some IL-1. is released extracellularly and exists as either a membrane-bound form or as a circulating 17 kDa molecule. When membranebound, membrane association is mediated either via a poorly-understood cell surface lectin interaction with the glycosylated IL-1. pro-form, or by interaction of myristoylated pro-IL-1. with plasma membrane phospho-lipids . When released as a 17 kDa soluble form, calpain initiates cleavage of the pro-IL-1. precursor . Unlike pro-IL-1., which is biologically inactive, both pro-IL-1. and mature IL-1. have been shown to be biologically active . Within the mature protein, rat IL-1. shares 79%, 60%, 59%, 58%, 57%, and 56% aa sequence identity with mouse, rabbit, human, bovine, canine and feline proteins, respectively . Mammalian cells known to express IL-1. include brown adipocytes , keratinocytes , monocytes , macrophages , endothelial and smooth muscle cells , mast cells , Schwann cells , as well as osteoblasts and osteoclasts . Three type I transmembrane immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1 R1), IL-1 receptor type II (IL-1 R2), and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1 RAcP, IL-1 R3)are involved in the formation of high affinity cell surface IL-1 receptor complexes. Both IL-1 R1 and IL-1 R2 can bind directly to IL-1.. IL-1 RAcP does not bind IL-1. directly, but interacts with IL-1 R1 in the presence of IL-1 to form the high-affinity receptor complex which is required for intracellular signal transduction. IL-1 RAcP also interacts with IL-1 R2 to form a non-functional high-affinity receptor complex that does not transduce IL-1 signals. Therefore, IL-1 R2 functions as a decoy receptor that attenuates IL-1. functions . IL-1. possesses a wide variety of biological activities and plays a central role in mediating immune and inflammatory responses. Normal production of IL-1. is critical for hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, osteoclast differentiation, and initiation of normal host responses to injury and infection(15,32-34). Inappropriate production of IL-1. has been implicated in the production of a variety of pathological conditions including sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis . |
| Gene Symbol | Il1a |
| Standard Curve |
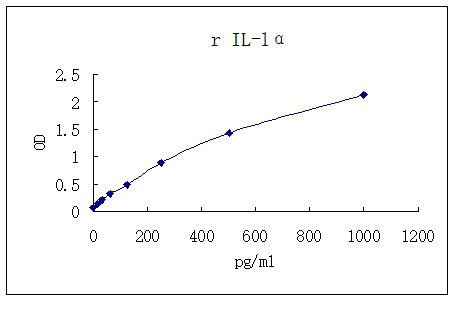
Representative standard curve for IL-1a ELISA. IL-1a was diluted in serial two-fold steps in Sample Diluent.
|
Documents
| Product Manuals |


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China

