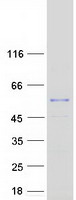
NDUFV1 (NM_007103) Human Mass Spec Standard
CAT#: PH304954
NDUFV1 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_009034)
View other "NDUFV1" proteins (3)
|
Need it in bulk or customized? Get a free quote |
CNY 19,520.00
CNY 3,080.00
CNY 6,281.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Description | NDUFV1 MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_009034) |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293 |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence | RC204954 |
| Predicted MW | 50.8 kDa |
| Protein Sequence |
>RC204954 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MLATRRLLGWSLPARVSVRFSGDTTAPKKTSFGSLKDEDRIFTNLYGRHDWRLKGSLSRGDWYKTKEILL KGPDWILGEIKTSGLRGRGGAGFPTGLKWSFMNKPSDGRPKYLVVNADEGEPGTCKDREILRHDPHKLLE GCLVGGRAMGARAAYIYIRGEFYNEASNLQVAIREAYEAGLIGKNACGSGYDFDVFVVRGAGAYICGEET ALIESIEGKQGKPRLKPPFPADVGVFGCPTTVANVETVAVSPTICRRGGTWFAGFGRERNSGTKLFNISG HVNHPCTVEEEMSVPLKELIEKHAGGVTGGWDNLLAVIPGGSSTPLIPKSVCETVLMDFDALVQAQTGLG TAAVIVMDRSTDIVKAIARLIEFYKHESCGQCTPCREGVDWMNKVMARFVRGDARPAEIDSLWEISKQIE GHTICALGDGAAWPVQGLIRHFRPELEERMQRFAQQHQARQAAS TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration | >0.05 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Labeling Method | Labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3 |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_009034 |
| RefSeq Size | 1631 |
| RefSeq ORF | 1392 |
| Synonyms | CI-51K; CI51KD; MC1DN4; UQOR1 |
| Locus ID | 4723 |
| Cytogenetics | 11q13.2 |
| Summary | The mitochondrial respiratory chain provides energy to cells via oxidative phosphorylation and consists of four membrane-bound electron-transporting protein complexes (I-IV) and an ATP synthase (complex V). This gene encodes a 51 kDa subunit of the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex I; a large complex with at least 45 nuclear and mitochondrial encoded subunits that liberates electrons from NADH and channels them to ubiquinone. This subunit carries the NADH-binding site as well as flavin mononucleotide (FMN)- and Fe-S-biding sites. Defects in complex I are a common cause of mitochondrial dysfunction; a syndrome that occurs in approximately 1 in 10,000 live births. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency is linked to myopathies, encephalomyopathies, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease and Leigh syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, Metabolic pathways, Oxidative phosphorylation, Parkinson's disease |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
| 蛋白相关资源 |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC416198 | NDUFV1 HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
CNY 900.00 |
|
| LY416198 | Transient overexpression lysate of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 1, 51kDa (NDUFV1), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 1 |
CNY 3,080.00 |
|
| TP304954 | Recombinant protein of human NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 1, 51kDa (NDUFV1), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, 20 µg |
CNY 2,900.00 |


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China